Insulin resistance is a growing health concern worldwide and is often a precursor to conditions such as type 2 diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases. It occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, a hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. In this blog, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and effective ways to manage insulin resistance to prevent long-term health complications.
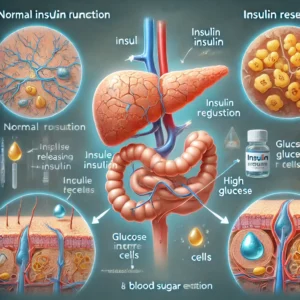
What is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps transport glucose from the bloodstream into the cells, where it is used for energy. When insulin resistance develops, cells do not respond effectively to insulin, causing glucose to remain in the blood. To compensate, the pancreas produces more insulin, leading to elevated insulin levels, which over time can contribute to prediabetes and type 2 diabetes.
Causes of Insulin Resistance
A variety of factors can contribute to insulin resistance, including:
- Poor Diet Choices
- High intake of refined carbohydrates, added sugars, and unhealthy fats can lead to insulin spikes and eventually insulin resistance.
- Sedentary Lifestyle
- Lack of physical activity reduces the body’s ability to use glucose efficiently, leading to insulin resistance.
- Obesity
- Excess weight, particularly visceral fat around the abdomen, increases inflammation and interferes with insulin function.
- Chronic Stress
- Prolonged stress leads to an overproduction of cortisol, which negatively impacts insulin sensitivity.
- Hormonal Imbalances
- Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and hypothyroidism are linked to insulin resistance.
- Genetic Predisposition
- A family history of diabetes or metabolic disorders can increase the risk of developing insulin resistance.

Symptoms of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance can develop silently, but some common warning signs include:
- Increased hunger and sugar cravings
- Fatigue, especially after meals
- Weight gain, primarily around the abdomen
- Dark patches of skin (Acanthosis Nigricans), commonly on the neck or armpits
- High blood pressure and cholesterol levels
- Brain fog and difficulty concentrating
- Frequent urination and increased thirst
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice and get tested for insulin resistance.
How to Diagnose Insulin Resistance
Healthcare providers diagnose insulin resistance through a combination of:
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test: Measures blood sugar levels after fasting overnight.
- Hemoglobin A1C Test: Provides an average blood sugar level over the past 2-3 months.
- Fasting Insulin Test: Evaluates insulin levels in the blood.
- HOMA-IR (Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance): A calculation used to estimate insulin resistance.
Effective Ways to Manage and Reverse Insulin Resistance
The good news is that insulin resistance can often be managed and even reversed through lifestyle changes and targeted strategies.
1. Adopting a Healthy Diet
A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in improving insulin sensitivity. Consider the following dietary strategies:
- Eat More Fiber: Foods such as whole grains, vegetables, and legumes help slow glucose absorption and improve insulin response.
- Choose Healthy Fats: Include sources like avocados, olive oil, and nuts to promote heart health.
- Limit Refined Carbs and Sugars: Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and white bread.
- Increase Protein Intake: Lean proteins like fish, chicken, and tofu can help stabilize blood sugar levels.

2. Engage in Regular Exercise
Exercise enhances insulin sensitivity and helps the body use glucose more efficiently. Recommended activities include:
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities like walking, running, and swimming improve cardiovascular health and insulin function.
- Strength Training: Building muscle mass enhances glucose uptake and insulin sensitivity.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Short bursts of high-intensity workouts can be highly effective in improving metabolic health.
3. Manage Stress Levels
Chronic stress contributes to insulin resistance by increasing cortisol levels. Techniques to reduce stress include:
- Meditation and mindfulness practices
- Deep breathing exercises
- Spending time in nature
- Ensuring adequate sleep (7-9 hours per night)
4. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Losing excess weight, particularly abdominal fat, significantly improves insulin sensitivity. Focus on sustainable weight loss through balanced nutrition and consistent physical activity.
5. Consider Supplementation
Certain supplements can support insulin function and overall metabolic health, such as:
- Berberine: A plant compound that helps lower blood sugar levels.
- Magnesium: Plays a role in insulin regulation and glucose metabolism.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Help reduce inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: May help lower post-meal blood sugar levels when consumed before meals.
Preventing Insulin Resistance
Preventing insulin resistance involves adopting long-term healthy habits, such as:
- Eating a nutrient-dense, balanced diet
- Staying active with regular exercise
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques
- Getting regular health check-ups to monitor blood sugar levels
Conclusion
Insulin resistance is a manageable condition, and with the right lifestyle changes, it can be reversed. By adopting a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress, you can improve your body’s insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases.
Take proactive steps today to support your metabolic health and prevent future complications.
